In this post, I would like to share all the common methods in python for data reconciliation. Consider scenarios like below: 1. Finding symmetric differences, 2. Combining data with overlaps. All the code below are for illustration purposes only, but the fundamentals can be scaled to more complex datasets.
import pandas as pdimport numpy as np# turn jupyter notebook warnings offimport warningswarnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
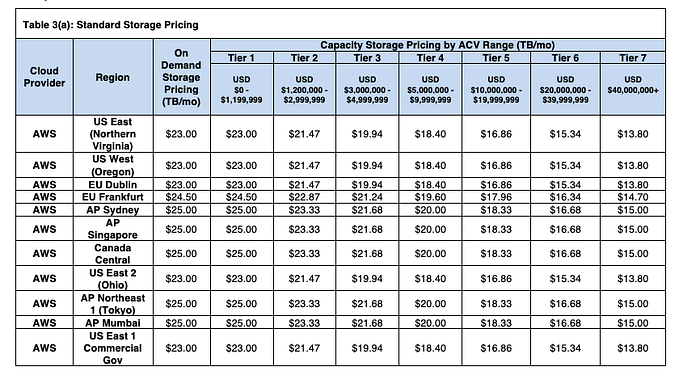
Working example one: Two dataframes with reconciliation column key containing non-duplicated elements
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'tradeid':range(5),'profit':range(1000,2000,200)})df2 = pd.DataFrame({'tradeid':range(2,7,1), 'stock': ['APL','MST','JNJ','TSL','BAB']})display(df1)display(df2)

Solution one: Since ‘tradeid’ is always unique, drop_duplicates() is the best way to spot the “exclusive-or” differences between two dataframes
pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=0).drop_duplicates(subset='tradeid',keep=False)
Solution two: Since ‘tradeid’ is always unique, we can also use a set function to find our differences
diff = set(df1.tradeid).symmetric_difference(set(df2.tradeid))Then use .isin() method to select the rows from a list. Also python set is not searchable by hash values; thus converting to list
pd.concat([df1.loc[df1['tradeid'].isin(list(diff)),:],df2.loc[df2['tradeid'].isin(list(diff)),:]])
Solution three: Similar to solution two, this time we are finding symmetric differences using np.array
diff = np.setxor1d(np.array(df1.tradeid), np.array(df2.tradeid))pd.concat([df1.loc[df1['tradeid'].isin(list(diff)),:],df2.loc[df2['tradeid'].isin(list(diff)),:]])

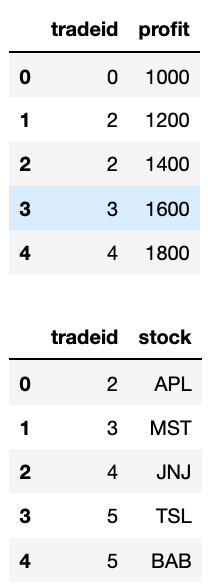
Working example two: Two dataframes with reconciliation column key containing duplicated elements
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'tradeid':[0,2,2,3,4],'profit':range(1000,2000,200)})df2 = pd.DataFrame({'tradeid':[2,3,4,5,5], 'stock':['APL','MST','JNJ','TSL','BAB']})display(df1)display(df2)
Solution: Use the pandas merge function with the indicator flag
df3 = df1.merge(df2, on='tradeid', how='outer', indicator=True)display(df3)df3 = df3.loc[df3["_merge"] != 'both', :]# cleanup to make df3 our final resultdel df3["_merge"]df3

Working example three: Finding symmetric differences for 2 lists containing duplicates
list1 = [0,1,1,2,3]
list2 = [0,1,3,4,4]Solution is embedded using functional programming
list3 = list(filter(lambda x:x not in list2, list1))
list4 = list(filter(lambda x:x not in list1, list2))list3 + list4Out: [2, 4, 4]
p.s. list comprehension does not work here somehow [list1.remove(x) for x in list1 if x in list2]
Working example four: Combining data with overlaps
d1 = pd.DataFrame({'tradeid':[0,1,2],'profit':[1000,np.nan,2000],'stock':['APL','JNJ',np.nan]})d2 = pd.DataFrame({'tradeid':[3,1,2],'profit':[1000,1500,np.nan],'stock':['APL',np.nan,np.nan]})display(d1)display(d2)
Subsequent dataset will combine and overwrite the original
oned2.combine_first(d1)